Fat Burning Cardio: Benefits, Program Options, Helpful Tips
Fat Burning Mechanism
In order for the process of losing weight to be as effective as possible, you need to understand how we lose kilograms and centimeters on the stomach and hips. After all, it happens like this: every day I worked out for two hours in the gym without a break, practically crawled to the house, but did not get the desired result. Let's face the facts: our body can use two types of energy:
- Fast (from ATP reserves, glycolysis).
- Slow (lipolysis, it is released due to the action of oxygen and enzymes on fat cells).
A fast source of energy is available only to trained people whose body is adapted to serious stress. Slow energy is released gradually (over 40-50 minutes). The metabolic rate of each person is individual, but metabolic processes can be improved through proper nutrition and regular exercise. That's why trained people are able to burn fat more easily. During cardio training, a large amount of oxygen enters the body, fat molecules are oxidized faster, and the process of losing weight is activated. We would like to remind you that if subcutaneous fat can be removed by adjusting your diet, then visceral (internal) fat is burned only by intense exercise.
Benefits and types of cardio training

What is cardio? This is a high-intensity physical activity when energy is obtained by glycolysis (glucose oxidation). Strength training produces energy in an oxygen-free way, all efforts are aimed at developing muscle mass, while cardio also improves the activity of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
When is the best time to do cardio? Training is best done when glycogen levels are low. Best after sleep or strength training. Cardio is a great way to energize all day and speed up fat burning. Work out outdoors or in a well-ventilated area, because this is an aerobic process (with the absorption of oxygen). Do not think that the more you sweat, the more weight you will lose. You will simply lose salts and minerals, and fat deposits will remain the same.
Benefits of cardio:
- Burning internal fat, inaccessible to diets.
- Proper distribution of loads will make the body more resilient.
- In addition to fat burning, metabolic processes are accelerated.
- Increased lung capacity and strength.
- Improving the work of the cardiovascular system.
- Effective stress and tension relief.
- A charge of vivacity and energy for the next day.
Exercises and loads in the form of swimming, running, walking, boxing, rowing, cycling, step aerobics, badminton, skiing and skating, jumping rope, etc.
Program options

Walking. In an hour, 300-400 kcal is burned, suitable for beginners, as well as people who are temporarily prohibited from serious loads. It doesn't matter which way you choose: walking in the park, in the gym on a treadmill, Nordic walking. The disadvantage of such training is low intensity. 15 minutes of cycling burns as many calories as 40 minutes of walking.
Run. For an hour, 600 kcal is burned. It is advisable to do jogging 3-4 times a week. To begin with, running at a constant speed is recommended, later you can move on to intervals - alternating fast walking with sprinting. Well stimulates metabolism, burns fat in the thighs and abdomen, develops aerobic endurance. The disadvantage is that it is not suitable for people with obesity and those who are contraindicated in the load on the knee joints. For beginners, the duration of the exercise is 20-30 minutes, at first you can alternate running with walking, gradually increasing the load.
Bicycle and exercise bike. You burn the same number of calories as running. The frequency is also three times a week, but less stress on the knees and the respiratory system. The duration of the exercise is up to 45 minutes.
Elliptical Trainer. For an hour of training, you can burn 600 kilocalories. It is not the calves that work more (as during running), but the muscles of the thighs and buttocks, the load on the knees is minimal. For beginners, exercises should last no more than 45 minutes.
Rowing. This is not only kayaks and canoes, but also a rowing machine in the hall. You can burn more kilocalories - 840 per hour. All muscle groups are included in the work: legs, arms, back, abdomen. True, such a simulator can not be found in every gym. The duration of the workout is 20-25 minutes.
Swimming. For an hour of exercise, you can spend 600 kcal, the minimum load on the spine, all muscle groups are involved, including the back and abdomen. Burning fat will be most effective if you exercise at least 3 times a week and master different styles.
jumping. An hour of exercise burns 1000 kcal, but there is an additional load on the calf muscles and arms. This is one of the most difficult types of cardio workout, do no more than 15 minutes as a warm-up, otherwise you can injure your knees.
HIIT. Constant change of activities. This is a complex program, but effective for burning fat. The body does not get used to the loads, as new muscle groups are constantly involved, metabolism increases, more calories are burned. Not recommended for beginners, should not be performed after strength training. Example: alternate step aerobics, running and cycling. Duration - up to 30 minutes, no more than 2 times a week. You need to take turns doing exercises with high and low intensity, without rest.
Measure heart rate and fat burning intensity
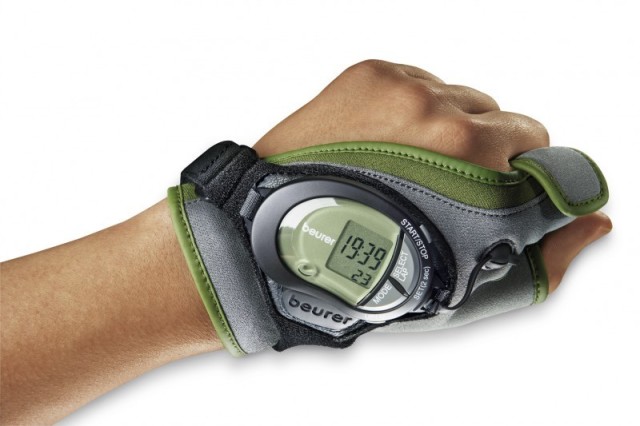

The intensity of the cardio program is:
- Low-intensity (up to 60% of heart rate - heart rate), low load on the joints, suitable for beginners.
- Medium-intensive (up to 75% heart rate) - used for active recovery after injuries, can be alternated with strength exercises.
- High-intensity (up to 85% heart rate) - speeds up metabolism, burns as many calories as needed, takes less time, but is not suitable for beginners.
How many times a week do you train? It is better to alternate cardio and strength exercises. In order for the training to be effective and not harm the body, you need to track the pulse.
Workout formula:
220 - age = maximum heart rate.
Normally, you should do exercises within 70-90% of your maximum heart rate. For example, for 30 years old, these are: upper: 220-30 \u003d 190X0.9 \u003d 171 beats per minute; lower: 220-30 \u003d 190X0.7 \u003d 133 beats per minute
Try to stay within this range, a heart rate monitor will help calculate the pulse. Over time, you will learn to feel your body. In addition, modern simulators have statistics: the number of calories lost, distance, pulse, and so on. You don't even have to do anything.







 Fat Burning Cardio: Benefits, Program Options, Helpful Tips
Fat Burning Cardio: Benefits, Program Options, Helpful Tips 7 most effective exercises for breast lift at home - a complex for women and girls
7 most effective exercises for breast lift at home - a complex for women and girls How to pump up at home in the shortest possible time?
How to pump up at home in the shortest possible time? Technique and important tips for doing the exercise
Technique and important tips for doing the exercise